Tree canopy coverage and heat maps – Middleton
The canopy cover and radiant temperature visualisation maps for Middleton are shown below:
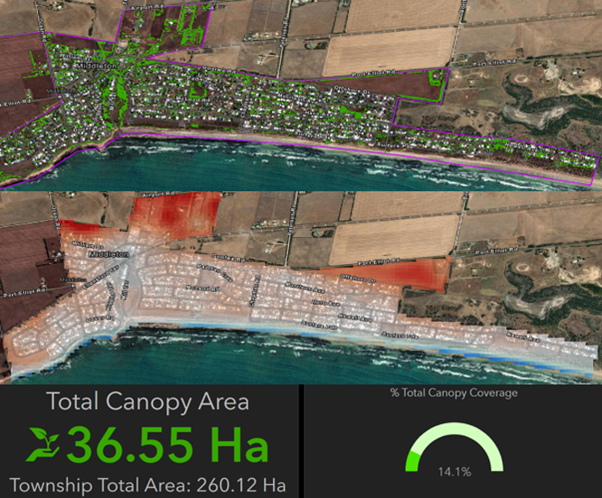 Aerial imagery showing Middleton’s canopy coverage on the top, and the heat map of the township (radiant temperature visualisation) on the bottom. Data was captured on 26 January 2022. © Active Green Services
Aerial imagery showing Middleton’s canopy coverage on the top, and the heat map of the township (radiant temperature visualisation) on the bottom. Data was captured on 26 January 2022. © Active Green Services
In 2022, Council commissioned a study to establish a benchmark of tree canopy cover and radiant temperature visualisation (‘heat maps’) across 11 townships in Alexandrina. The study assessed high-resolution satellite imagery using artificial intelligence. Thermal imaging (infrared) was also acquired and correlated to the canopy layer by linking the data geospatially via an ESRI© application.
The overall canopy cover averaged 17.6% across Alexandrina’s 11 townships; ranging from 11.7% to 49.3%.
The study showed that in January 2022, Middleton had a tree canopy cover of 14.1%.
The results for Middleton are as follows:
Tree canopy cover across Middleton
The township total area of Middleton is 260.12 hectares (ha), with 36.55ha identified as the total canopy area. This equates to 14.1% total canopy coverage in Middleton.
Tree canopy cover on private land
Most of the land in Middleton is privately owned: 156.98ha of the township total area is private land, with 24.41ha of this contributing to the total canopy area. This means that 66.79% of the total canopy cover is found on private land.
Tree canopy cover on Council land
31.40% of the total canopy cover is on Council land: 99.26ha of the township total area is under Council’s care and control, with 11.48ha contributing to the total canopy area.
Tree canopy cover on Crown land
A very small percentage of land is Crown land: 3.88ha of the township total area is on Crown land, with 0.66ha of this contributing to the total canopy area. This equates to 1.81% total canopy coverage in Middleton.
Radiant temperature of Middleton
The radiant temperature visualisation (‘heat map’) undertaken for Middleton (see above) clearly shows the cooling effect that tree canopies and the ocean provide.
The hottest areas are found in paddocks as relative radiant temperature of open parks and fields can be high compared to treed areas.
It is important to note is that radiant temperatures are not air temperatures. Satellite sensing is typically done at night. Radiant heat is measured as infrared spectral intensity and expressed as temperature mathematically, through prior research using controlled experiments correlating the influence of surface temperatures on perception of heat by a collective of people.
To go back to the main page of the Tree Canopy Report and links to other townships, click here.
